Cnc Threading Program

CNC Training, Rose Training, Swiss-Turning, Fundamental CNC, Tooling & Production Tooling & Production October 2003 'Shop Talk with Steve Rose' G32 - Threading with Control In this space we've talked about using G76, a canned cycle threading command that is easy to program. Spongebob Season 1 Episode 1 Subtitles. Another popular threading command is G32. The G32/G33 method is the traditional thread programming command.
May 27, 2015 This video shows the format of the G76 and G92 Threading Cycles used on a CNC lathe with Fanuc controls. Jul 29, 2013 CNC Machining; thread programming on lathe; Results 1 to 6 of 6 Thread. It said that it is better to write a custom program for threading? Threading Methods There are three programming methods available for programming on Fanuc based controls. We’ll look at the benefits of each. CNC machining center thread milling software for standard, NPT pipe, and other tapered thread requirements Email info@advancedCNCsolutions.com for a 30 day trial program.
It is often output from CAD/CAM software packages when you ask for a threading routine. Although CAD/CAM software makes programming easier, it is always helpful to understand the codes and exactly what they mean.
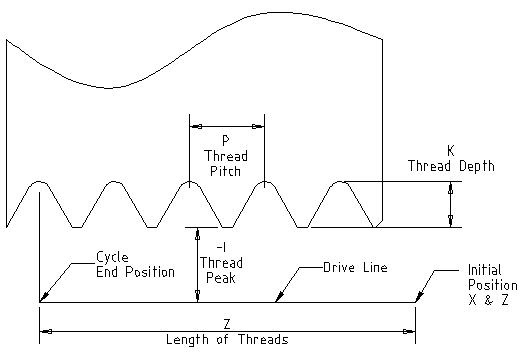
Let's take a look at the G32 threading program. The two biggest advantages to the G32 method are that you, as the writer, can control the depth of each thread pass and the exact plunge angle. To cut a thread, the tool makes many passes, taking shallow cuts down the angle of the plunge. In our example, we'll program a 4' diameter, 12-pitch thread, 2' long.
As the programmer, you must determine the X and Z positions for each pass. The first step is to determine the plunge angle at which the insert approaches the part. We are using a 29˚ angle in our example. Next, at what Z position will the tool start to make the first pass? To allow for the acceleration of the Z axis slide, we normally start the routine approximately 4 pitches from the beginning of the thread feature. We are programming a 12-pitch thread, so we have started at the Z0.400 position. Fontlab Studio 5 Crack. Tooling manufacturer supply recommendations for the depth of each pass.
This information is generally found in the tooling catalogs. The tooling catalogs reveal that the depth of each pass gets smaller as you approach the final thread depth (the minor diameter). As the tool gets deeper into the thread, the area of contact between the part and the tool increases. Taking more shallow cuts allows for this increase in contact and reduces the chance for work hardening. Now, we know the Z start point for the first thread pass and the X dimension for each pass (depth of each cut), but we do not know the Z position for each pass. A simple trig calculation provides this value. Tinlicker Remember The Future there.